Medicine and Biotechnology
Medicine and Biotechnology
Registry Entry: PI No. FS77-88898 dated 13.12.2024
Founder and publisher
Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “National Research Ogarev Mordovia State University”
Editor-in-Chief
Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "National Research Ogarev Mordovia State University"
Editor-in-Chief
Larisa A. Balykova
Vice-Rector for Innovation in Biotechnology and Medicine
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Frequency / Access
4 issues per year / Open Access
Official Journal Website:
The peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal Medicine and Biotechnology aims to acquaint readers with the results of original scientific research that contribute to the advancement of science in the fields of medicine and biotechnology.
Mission
The journal’s mission is to serve as an international platform for scholarly discussion, exchange of experience, and dissemination of current achievements in medicine and biotechnology.
Audience
The journal is intended for researchers and professionals in the fields of medicine, pharmacology, biology, biomedicine, and veterinary science; for faculty members, postgraduate students, and undergraduate students of higher education institutions; as well as for a broader readership interested in promising areas of Russian and international science.
Peer Review Policy
All submitted articles undergo scientific peer review (double-blind). Each manuscript is reviewed by several leading experts whose academic specialization closely aligns with the subject matter of the article.
Anti-Plagiarism Policy
The editorial board upholds a zero-tolerance policy toward plagiarism. All manuscripts are checked for improper citation and originality using the “Antiplagiat” system.
Distribution
Russian Federation and international markets.
Open Access Policy
The journal provides open access to full texts of publications based on the principle that free access to research results promotes global knowledge exchange.
Journal Scope
The thematic focus of the journal corresponds to the following academic specialties and scientific disciplines as defined by the List of Peer-Reviewed Scientific Publications:
- 1.5.6. Biotechnology (biological, pharmaceutical, medical sciences)
- 3.1.9. Surgery (medical sciences)
- 3.1.18. Internal Medicine (medical sciences)
- 3.1.21. Pediatrics (medical sciences)
- 3.3.3. Pathophysiology (medical, biological sciences)
- 3.3.6. Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacology (medical, pharmaceutical, biological sciences)
Current Issue
Vol 1, No 3 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 22.09.2025
- Articles: 9
- URL: https://medbiosci.ru/MedBiotech/issue/view/19420
Full Issue
Editorial Article
 202-205
202-205


Pathological physiology
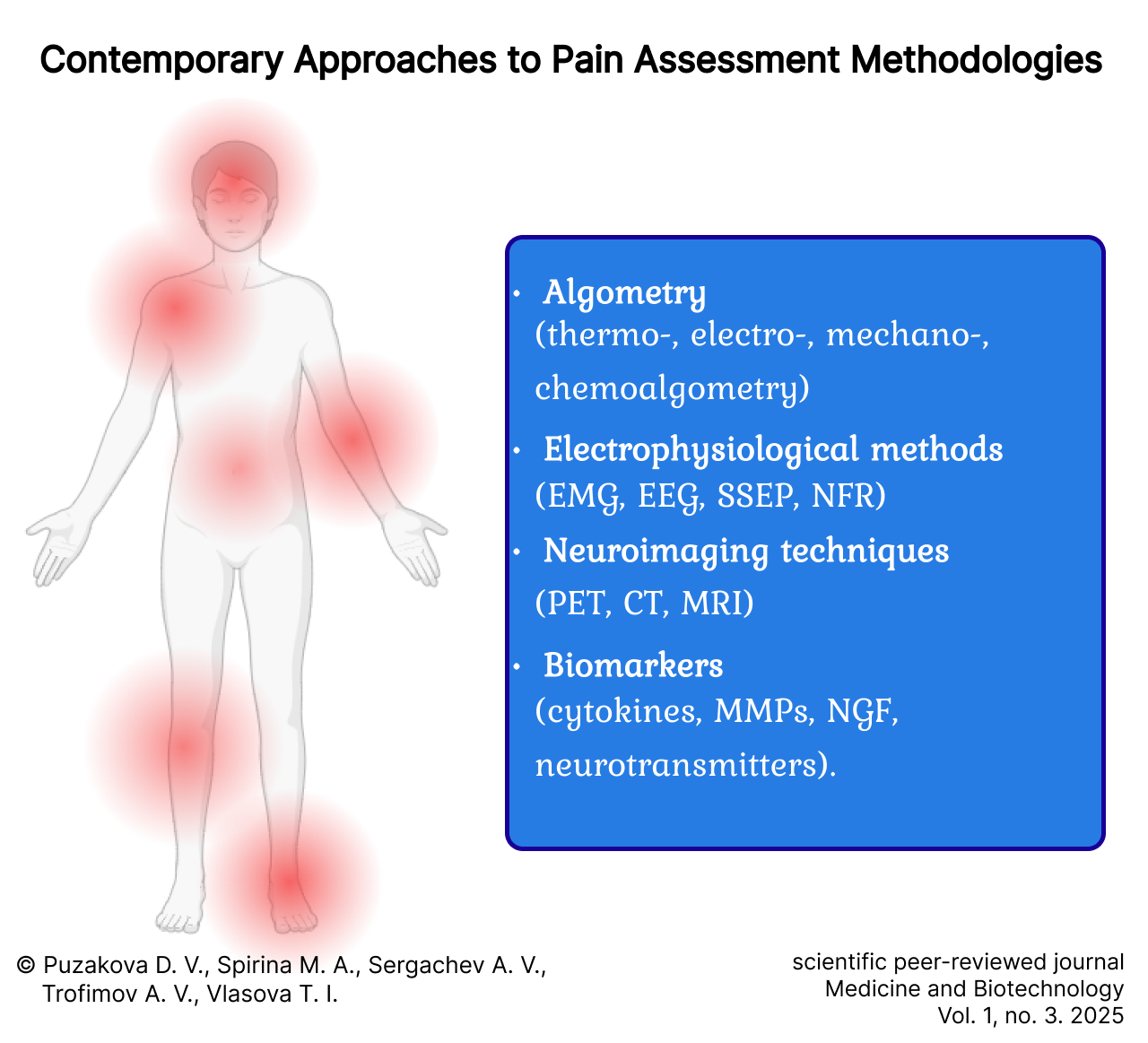
Contemporary Approaches to Pain Assessment Methodologies
Abstract
Introduction. Pain is a widespread medical issue that can lead to prolonged disability. Most studies assessing pain have relied on subjective evaluation methods; however, to accurately determine pain intensity, monitor treatment efficacy, and track the progression of chronic pain syndromes, objective and reliable assessment techniques are essential. The aim of this study is to generalize the most objective quantitative methods for analyzing chronic pain.
Materials and methods. The present review provides an analysis of international and domestic scientific publications focusing on contemporary methods of pain diagnosis. The literature search was conducted in open-access electronic databases, including PubMed and eLibrary. The primary selection criteria were the relevance of the information presented in the analyzed publications and their publication date, as this study emphasizes research conducted within the last decade. This article provides an analysis and the synthesis of the findings of existing studies to identify key trends and patterns in the field of pain diagnostics.
Results. Instrumental techniques for assessing the severity of pain syndrome are described, including algometry and neurophysiological methods, particularly electromyography. The potential application of electroencephalography for the objective evaluation of pain is also discussed. The use of somatosensory and laser-evoked skin potentials appears promising. The capabilities of computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography in the study and diagnosis of pain are presented. A number of potential biochemical markers of pain syndrome are described – substances whose elevated concentrations reflect pain intensity, such as proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. Several compounds influencing the function of both the central and peripheral nervous systems may be considered promising biomarkers for the objective quantification of pain.
Discussion and conclusion. The expansion and standardization of novel approaches to the quantitative assessment of pain syndromes will facilitate early diagnosis, enable the monitoring of pain progression, and provide an objective evaluation of therapeutic efficacy.
 206-223
206-223


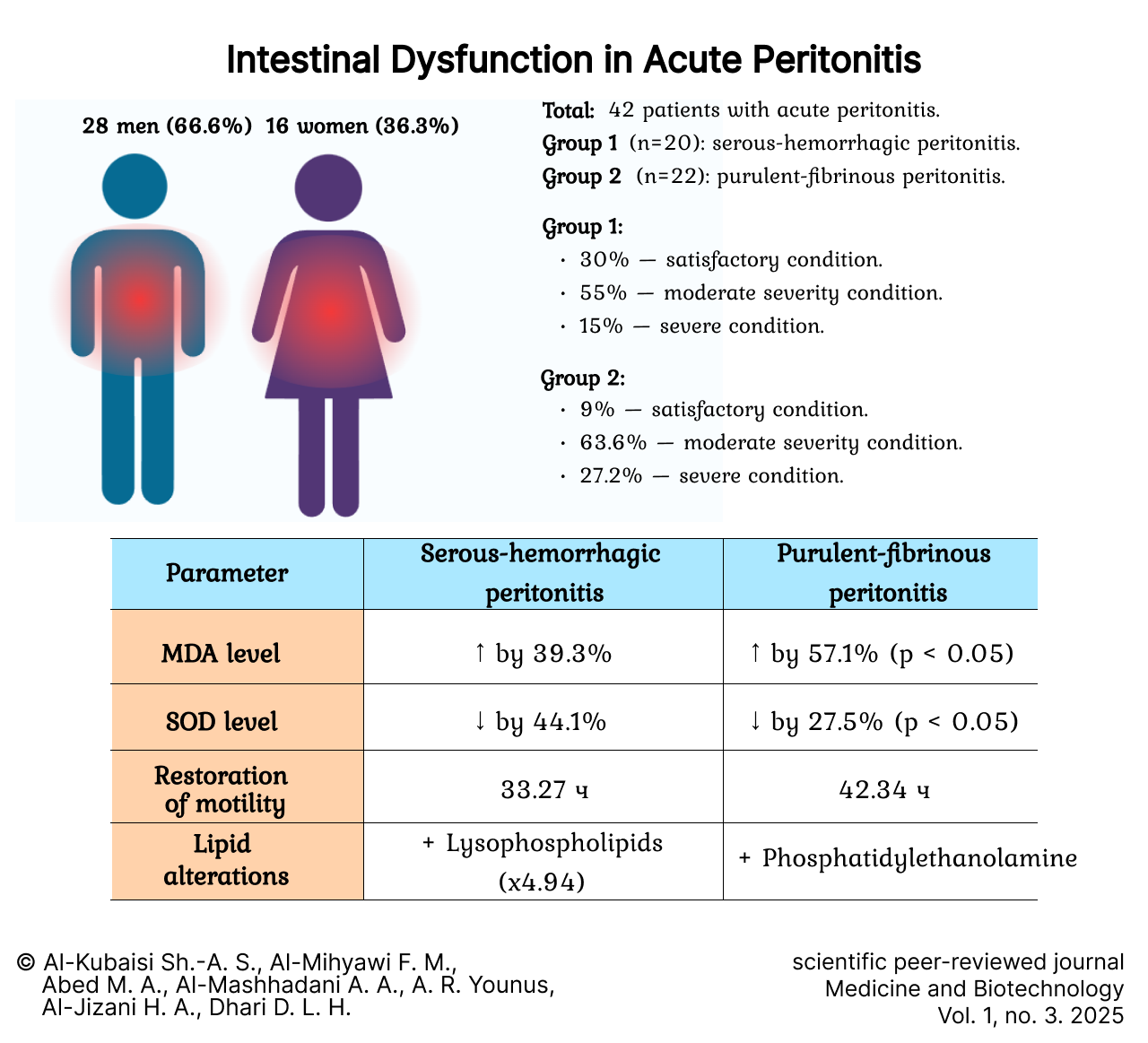
Intestinal Dysfunction in Acute Peritonitis
Abstract
Introduction. Acute peritonitis continues to be a significant medical issue because of its high mortality, especially in the terminal phase. The aim of this research is to define the role of lipid peroxidation processes in the disruption of small bowel function among patients with acute peritonitis.
Materials and methods. A clinical study included 42 patients with acute peritonitis. The morphofunctional state of the intestine was studied: in the first group (20 patients) with acute serous-hemorrhagic peritonitis, and in the second group (22 patients) with purulent-fibrinous peritonitis. The following methods were used in the study: determination of the oxidation-reduction potential, venous gradient using the Landis method, tissue oxygen diffusion coefficient, blood filling of the small intestinal tissues, lipid extraction from small intestinal tissues, content of diene conjugates and malondialdehyde, and superoxide dismutase activity.
Results. An evaluation of the morphofunctional state of the small intestine in patients with acute peritonitis revealed that the severity of alterations in the homeostasis system depended on the form of the disease. It was found that a key pathogenetic mechanism in acute peritonitis leading to impaired intestinal function was the activation of membrane-destabilizing processes. These processes induce significant disturbances in lipid metabolism, particularly within the lipid bilayer of cellular structures. It was established that membrane-destructive phenomena in acute peritonitis are accompanied by the activation of lipid peroxidation processes and a reduction in the antioxidant potential of enzymes.
Discussion and conclusion. In acute peritonitis, activation of lipid peroxidation processes is observed. This leads to impairment of small intestine function on the one hand, and to progression of the disease and complications on the other. The severity of changes in the morphofunctional state of the intestine depends on the severity of peritonitis.
 224-231
224-231


Pharmacology, clinical pharmacology
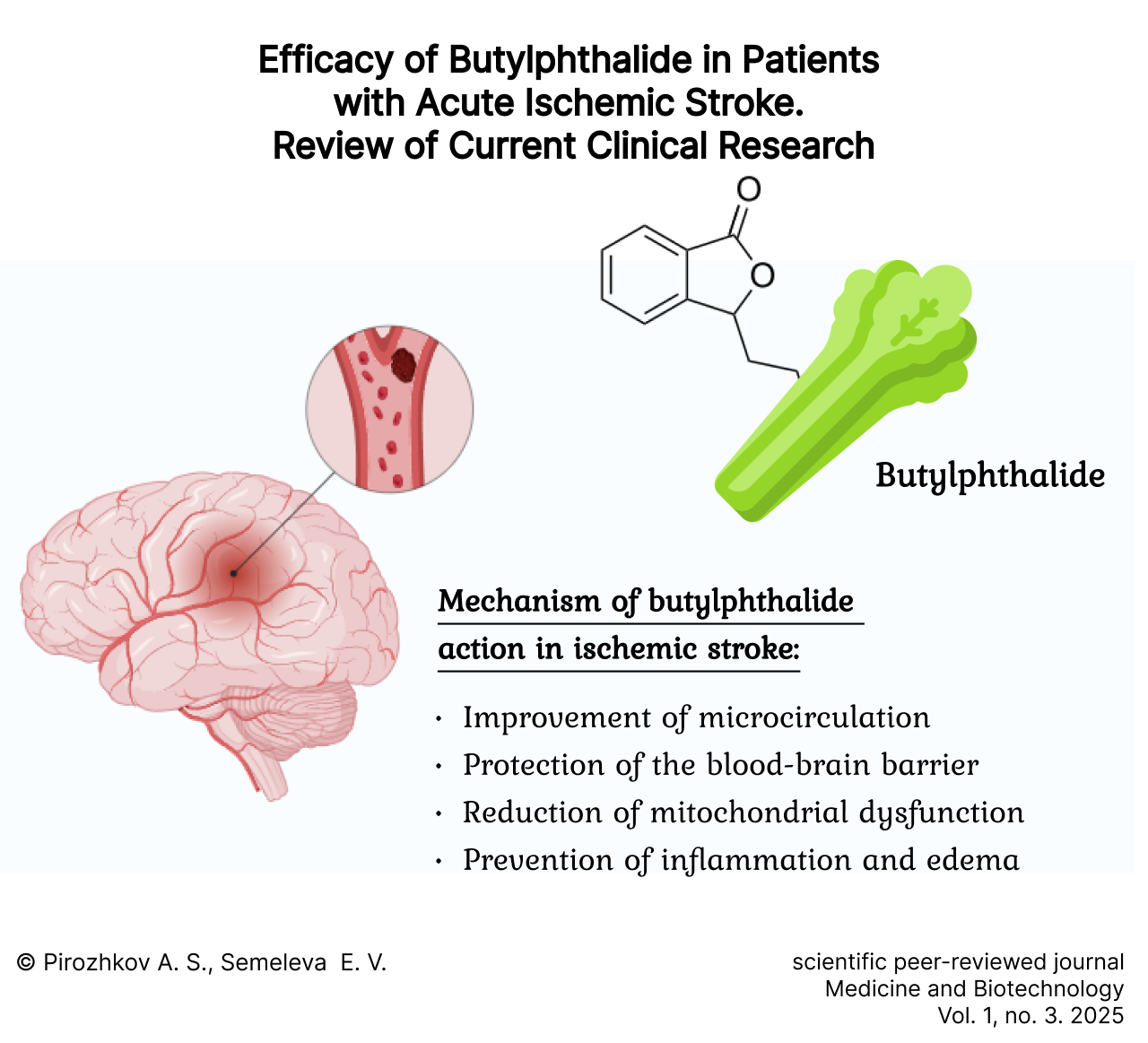
The Efficacy of Butylphthalide in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Clinical Evidence
Abstract
Introduction. Ischemic stroke constitutes one of the principal causes of global disability and mortality. Certain investigations have demonstrated that DL-3-n-butylphthalide exerts a significant neuroprotective effect in the context of cerebral ischemia. The aim of the study is to evaluate the efficacy of butylphthalide in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Materials and methods. A review of publications was conducted using the PubMed and ScienceDirect scientific databases. Consideration was given to the year of publication, with preference accorded to articles from the last decade. The inclusion criteria excluded non-randomized studies, investigations examining the effects of butylphthalide in combination with other pharmaceuticals, and research not specifically focused on patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Results. The selected studies enrolled exclusively Chinese patients, with a total cohort of 2,622 individuals. Therapeutic efficacy was assessed by monitoring the dynamics of neurological deficit using the US National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale and by evaluating the recovery of functional independence in daily living according to the Barthel Index. The data obtained at various stages of treatment have been compiled into tables.
Discussion and conclusion. The data from the studies reviewed herein indicate that butylphthalide is efficacious when administered early to patients experiencing ischemic stroke. However, definitive confirmation of its clinical significance necessitates further large-scale, multi-center trials with extended follow-up periods. These trials must encompass not only Chinese populations but also diverse ethnic groups.
 232-241
232-241


Internal medicine
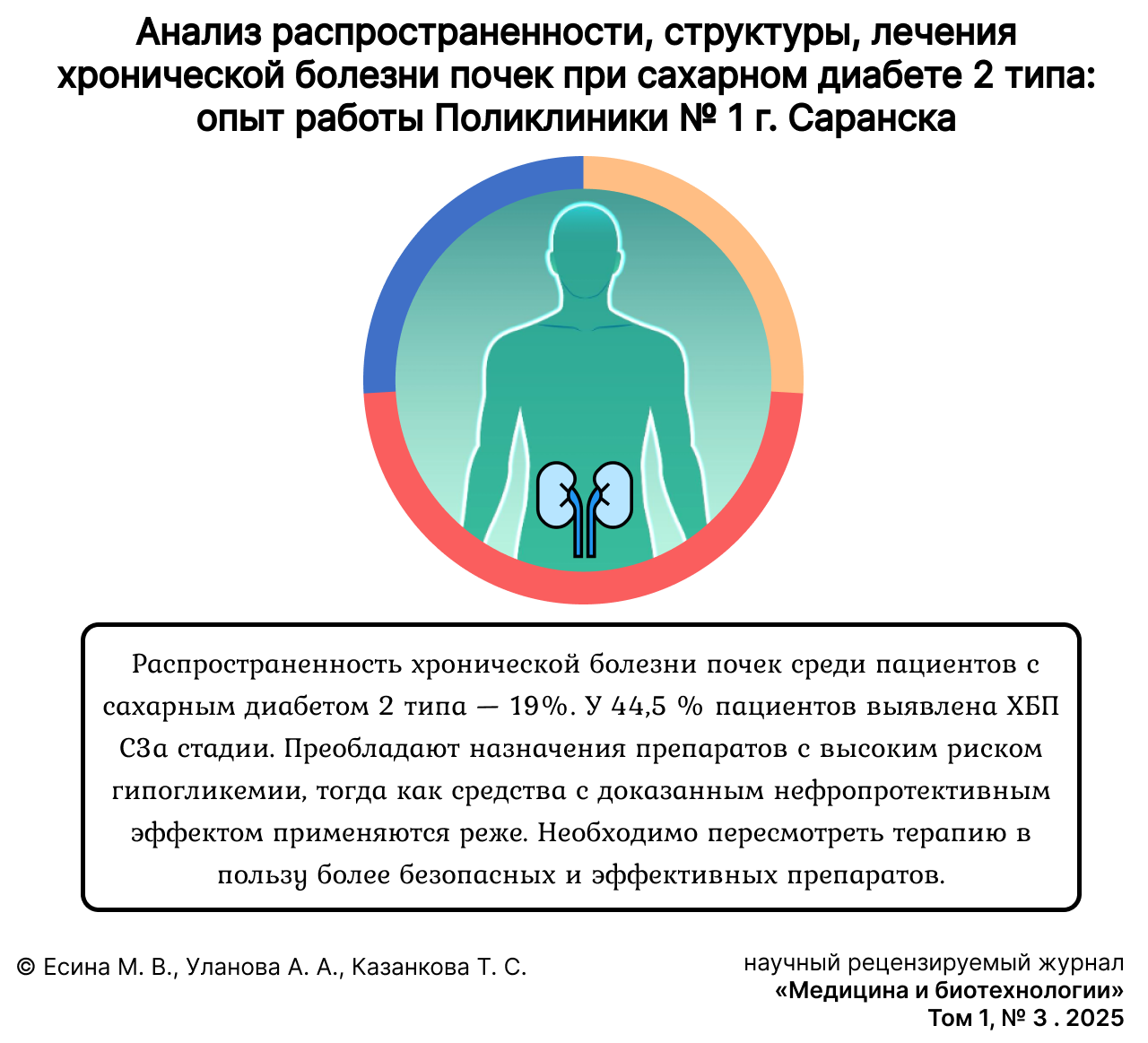
Analysis of Prevalence, Structure, Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Introduction. Chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus represent significant medical and societal challenges, owing to their high prevalence, associated disability and mortality rates, and the substantial economic costs of treatment. The objective of this study is to assess the prevalence, profile, and management of chronic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with the aim of optimising therapeutic strategies for affected individuals.
Materials and methods. A retrospective analysis was conducted of the prevalence, structure, and treatment of chronic kidney disease, alongside the status of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, based on the diabetes registry database of Polyclinic No. 1 in the city of Saransk for the year 2024.
Results. It has been established that the prevalence of chronic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is 19.07%. The majority of patients were diagnosed with stage 3 chronic kidney disease. Monotherapy with glucose-lowering agents was administered to 39.5% of patients, insulin therapy to 41.6%, and combined glucose-lowering therapy to 18.9%. Antihypertensive therapy was received by 63% of patients, with β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and angiotensin II receptor blockers being predominantly prescribed. Correction of lipid metabolism disorders with statins was performed in only one-third of the patients.
Discussion and conclusion. It was established that nearly half of the patients were diagnosed with chronic kidney disease at stage C3a (44.5%). A larger proportion consists of patients receiving glucose-lowering drugs with a high risk of inducing hypoglycemia, whereas a smaller proportion comprises those administered medications with a proven nephroprotective effect combined with cardiovascular safety. From the acquired data, it is necessary to conclude that a correction of the glucose-lowering therapy is required, prioritising the use of effective and safe hypoglycemic agents.
 242-251
242-251


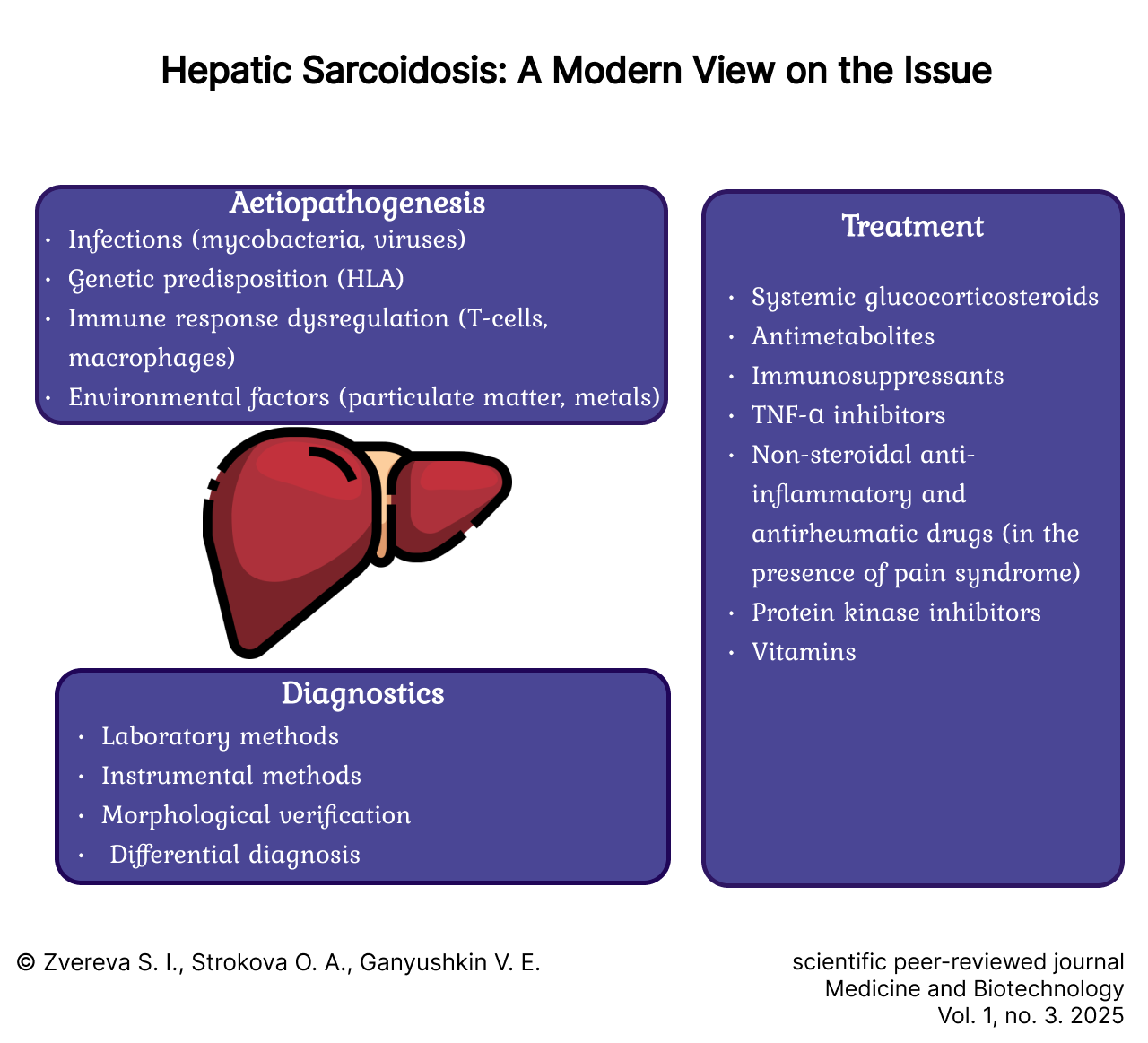
Hepatic Sarcoidosis: A Modern View on the Issue
Abstract
Introduction. Hepatic sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of non-caseating nodules (granulomas) in the liver tissue and associated functional impairments. Available data indicate the necessity of continuing research to clarify the mechanisms underlying the development of this pathology and to develop innovative treatment methods. The aim of this study is to analyze current scientific data on the epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, and treatment strategies for hepatic sarcoidosis.
Materials and methods. The following scientific databases were utilized: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and eLibrary. The search was conducted using keywords. Forty-eight publications were selected and analyzed: original articles, reviews, clinical cases, and meta-analyses published in English and Russian.
Results. Hepatic sarcoidosis is distinguished by a significant degree of heterogeneity and by the complex mechanisms underlying the formation and regression of granulomatous foci. The necessity of an interdisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management of this disease has been clearly demonstrated. Investigation into the pathogenetic influence of cytokines and chemokines unveils promising avenues for the development of pharmaceuticals aimed at modulating inflammation and inducing remission. The application of advanced imaging and molecular techniques is crucial for the early detection of hepatic involvement and for the prevention of complications. Key objectives for future research entail the development of highly efficacious therapeutic agents with low toxicity profiles.
Discussion and conclusion. The obtained results highlight the promise of a more detailed analysis of inflammatory processes in hepatic sarcoidosis, with a particular focus on the role of the immune system and potential targets for pharmacotherapy. The importance of integrating various disciplines and fostering a multidisciplinary approach to the study of this pathology is emphasised. Advances in understanding the pathophysiology of hepatic sarcoidosis, coupled with the introduction of novel diagnostic technologies and pharmaceutical agents, are poised to significantly improve patient management strategies. The proposed research directions pave the way for the development of a personalised approach to each patient, one that minimises the risks of therapy-related adverse effects and improves disease outcomes.
 252-268
252-268


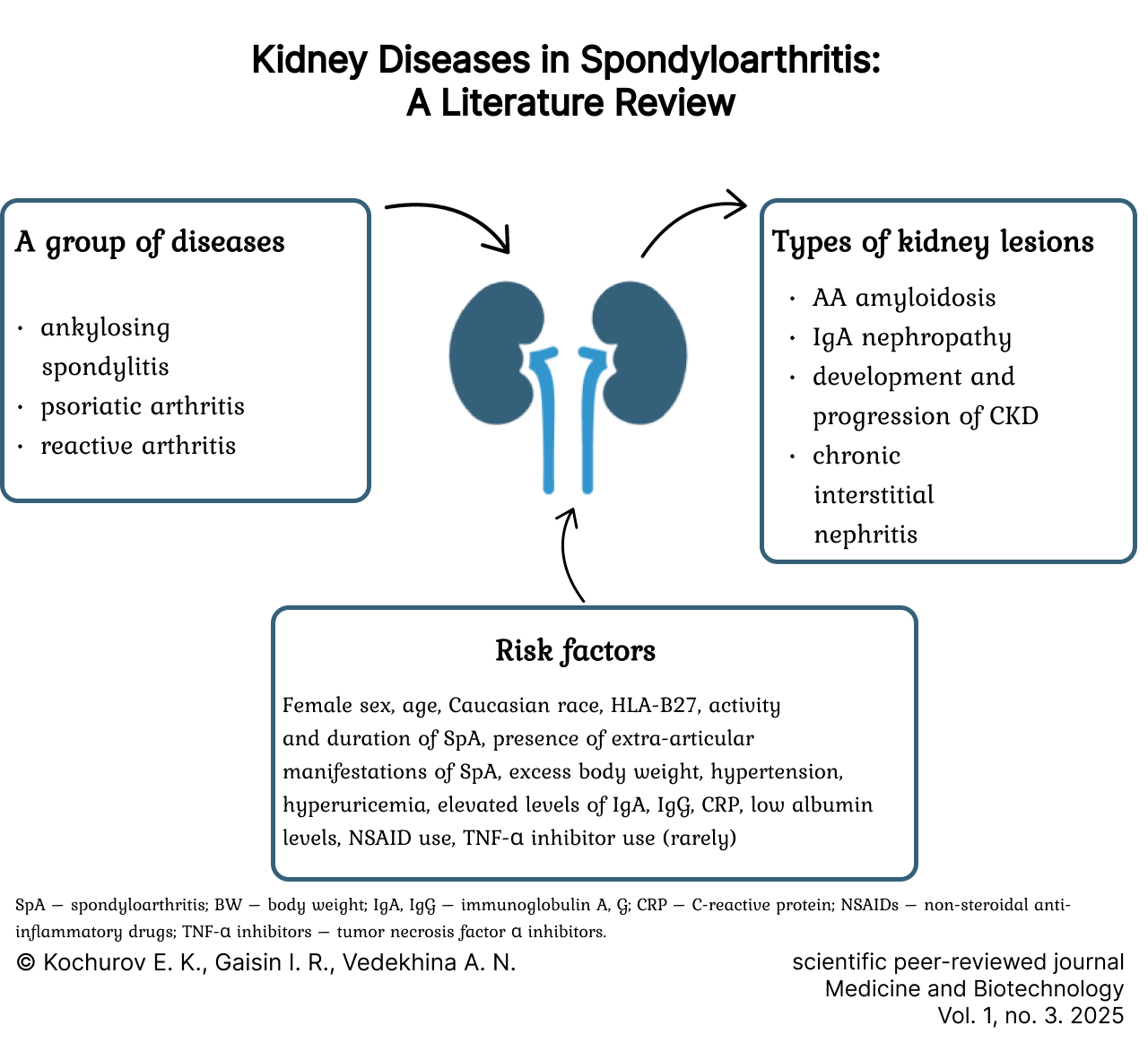
Kidney Involvement in Spondyloarthritis: A Literature Review
Abstract
Introduction. Currently, the identification and prevention of renal dysfunction in patients with spondyloarthritis receive insufficient attention, although kidney involvement can significantly determine their prognosis. The aim of this review is to analyze the types, prevalence, and risk factors for the development and progression of renal impairment in spondyloarthritis.
Materials and methods. A search for publications was conducted in the PubMed database using keywords for the period 2000–2024. Preference was given to original research, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses. Particular attention was paid to studies including kidney biopsy data, as well as works devoted to long-term patient follow-up. In addition, reference lists of review articles were examined to identify relevant publications. Ultimately, 66 studies were included in the review.
Results. Kidney involvement is a frequent complication of spondyloarthritis. The most common manifestations are AA amyloidosis, immunoglobulin A nephropathy, and chronic interstitial nephritis. Furthermore, patients are characterized by a significant prevalence and a greater risk of developing chronic kidney disease. High disease activity and duration, the presence of extra-articular manifestations, patient sex and age, time of diagnosis, the presence of human leukocyte antigen B27, and the levels of C-reactive protein, uric acid, immunoglobulins A and G, and albumin may indicate a high risk of kidney involvement.
The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, certain synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs may be associated with the development of kidney diseases, particularly in the presence of risk factors such as pre-existing renal dysfunction and hypertension. Metabolic disorders have a significant impact on the development and progression of renal dysfunction. Kidney dysfunction, in turn, affects adipose tissue function and the progression of metabolic disorders.
Discussion and conclusion. Routine examination of patients with spondyloarthritis is necessary to detect kidney involvement, as well as to identify and correct factors contributing to the development and progression of renal dysfunction in this patient group.
 269-285
269-285


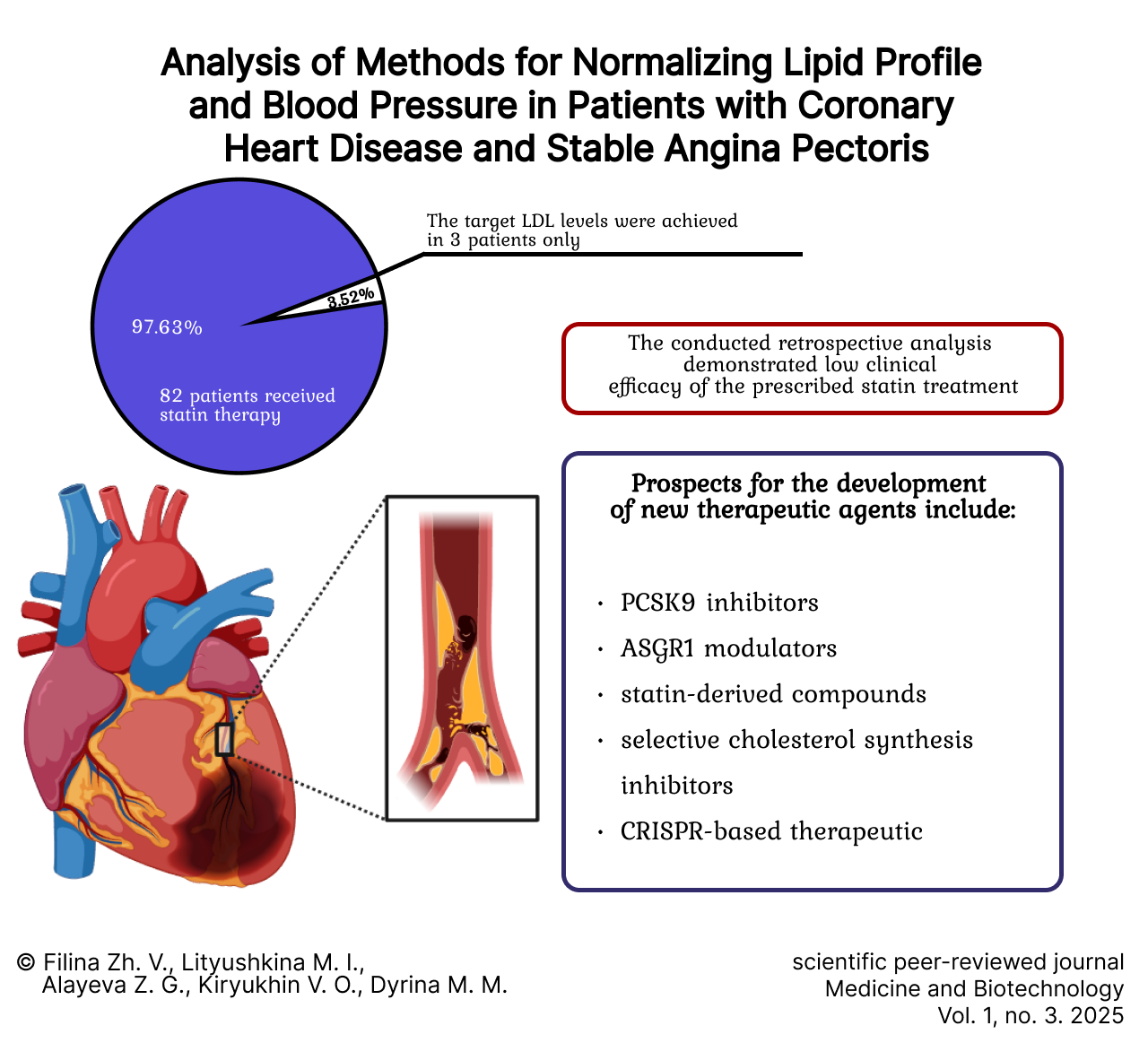
Analysis of Methods for Normalizing Lipid Profile and Blood Pressure in Patients with Chronic Coronary Syndromes
Abstract
Introduction. Despite advancements in modern cardiology, cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death in the Russian Federation and worldwide. A key predictor of these diseases is hyperlipidemia. Current treatment strategies involve increasingly aggressive lipid-lowering therapy to achieve target levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides. The aim of this study is a comprehensive investigation of the major risk factors for the development of ischemic heart disease and an analysis of the drug therapy used in patients with chronic coronary syndromes.
Materials and methods. We studied 85 outpatient medical records of patients with established diagnoses of “Stable exertional angina” and “Post-infarction cardiosclerosis” aged between 40 and 85 years (the mean age of participants was 65.27 (±1.02) years; 49 men and 36 women). Patients with acute coronary syndromes were not included in the study. The study was conducted through a retrospective analysis of outpatient medical records.
Results. Studying the processes of plaque formation in blood vessels (atherogenesis) and the influence of various risk factors (e.g., smoking, obesity, diabetes, arterial hypertension) helps to better understand the pathophysiology of the disease and develop effective preventive measures. The analysis revealed insufficient efficacy of the ongoing statin therapy in this patient group, as the target levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were not achieved. Modern treatment methods include lifestyle modifications, dietary therapy, and the use of pharmacological agents (statins, ezetimibe, bile acid sequestrants, fibrates). However, the effectiveness of these approaches is limited, particularly in severe cases of familial hypercholesterolemia. Therefore, further research is necessary to develop new therapeutic strategies, such as PCSK9-inhibiting monoclonal antibodies and drugs that reduce cholesterol synthesis in the liver. The development of personalized treatment approaches based on individual patient characteristics (genotype, phenotype, comorbidities) will improve therapy efficacy and reduce drug side effects.
Discussion and conclusion. Analysis of retrospective data obtained from outpatient records revealed the treatment strategies employing lipid-lowering drugs (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin) used in the patients. Out of 85 patients, 82 (97.64%) received statins. Only 3 patients (3.52%) achieved the target levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The conducted retrospective analysis demonstrated the low clinical efficacy of the prescribed statin therapy. The prospects for developing new drugs to treat hypercholesterolemia are focused around several key areas: PCSK9 inhibitors (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors), ASGR1 modulators (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 modulators), statin derivatives, selective cholesterol synthesis inhibitors, and therapies using the “genomic scissors” technique (e.g., CRISPR-based approaches). The presented research perspectives create the prerequisites for developing an individualized management algorithm for each patient. This approach has the potential to significantly minimize the likelihood of adverse drug reactions and optimize the clinical outcomes of the treatment process.
 286-297
286-297


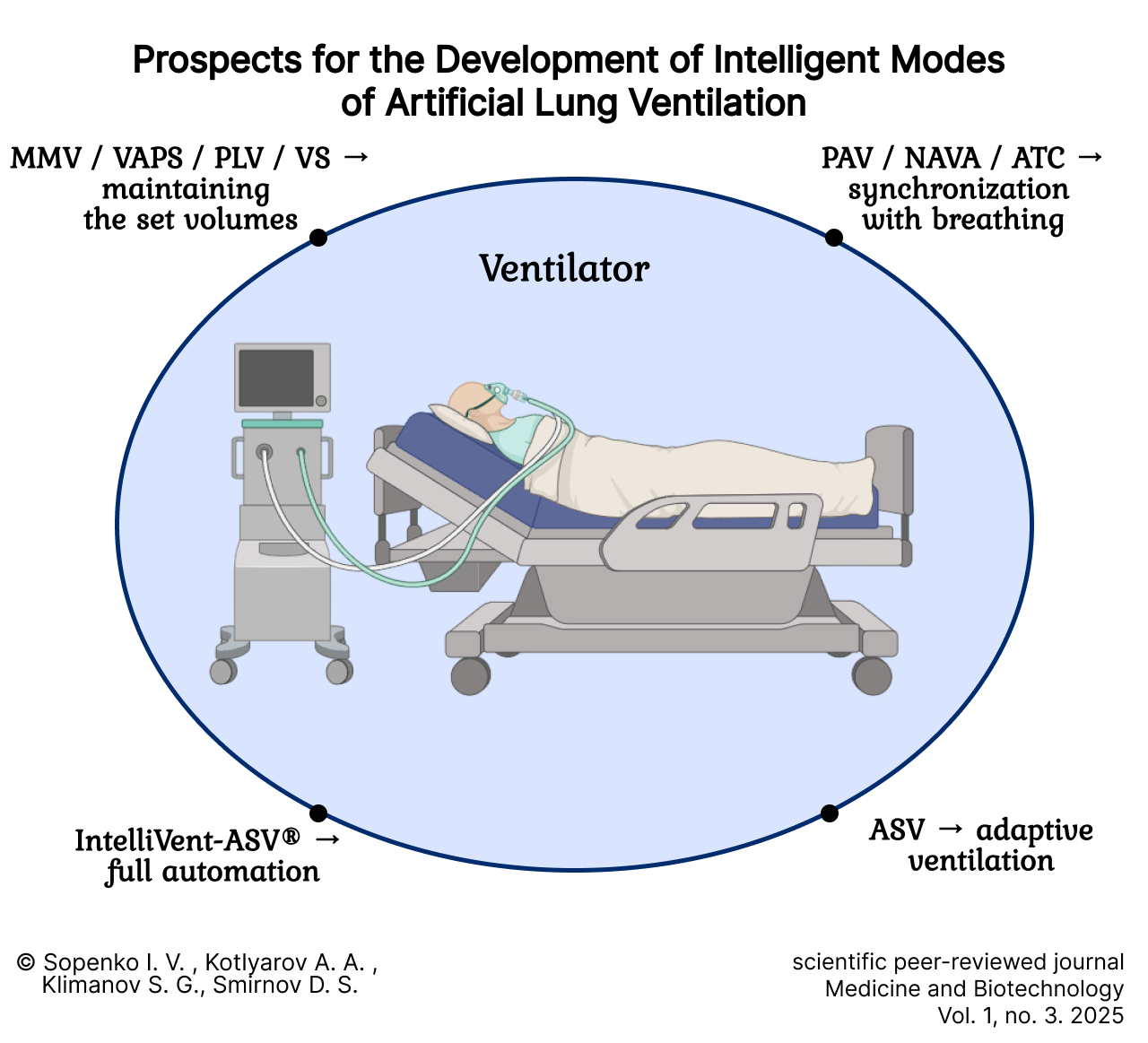
Prospects for the Development of Intelligent Mechanical Ventilation Modes
Abstract
Introduction. In modern clinical practice, mechanical ventilation is not only a primary method of intensive care for severe respiratory disorders of various origins but also a method of palliative therapy for patients with severe chronic respiratory failure. Consequently, there is a continuous pursuit of new ventilation modes capable of providing the most physiological and safe respiratory support for patients with various types of respiratory dysfunction. The aim of this review is to evaluate the intelligent modes of mechanical ventilation available in medical practice.
Materials and methods. A literature search was conducted in the following electronic scientific databases: PubMed, Google Scholar, and eLibrary. Article selection was performed using relevant keywords. To enable a comparative analysis of the intelligent mechanical ventilation modes presented in the medical literature, including their advantages and disadvantages over other existing modes, the review also incorporated data from relevant clinical practice guidelines and medical textbooks.
Results. Currently, there is a notable expansion in the range of mechanical ventilators being employed in clinical practice. This trend is accompanied by a proliferation of devices offering similar functionality under different commercial names, a factor that healthcare professionals must account for in their practical work. Conversely, the growing complexity of mechanical ventilation modes and techniques contributes to an increased workload and potential cognitive overload for intensive care unit staff.
Discussion and conclusion. Despite the expanding range of mechanical ventilators employing various assisted modes of respiratory support, the need persists for the development of a fully automated mechanical ventilation control system. Such a system must be capable of providing maximum adaptation of the ventilation mode to the changing parameters of a patient's respiratory function. It must be able to both autonomously select optimal modes and parameters for mechanical ventilation and, when interacting with the user, present a selection of potential corrective adjustments.
 298-306
298-306